The journey to parenthood is often filled with both excitement and uncertainty, especially when fertility challenges arise. For some, uterine abnormalities may complicate the process, bringing added worry and concern. While these conditions can feel daunting, understanding their impact on fertility is a crucial step toward finding your way forward.
In this article, we’ll look at common uterine abnormalities, how they affect conception, and the various fertility treatments available to support your family-building goals. From intrauterine insemination (IUI) to in vitro fertilisation (IVF) options here in Singapore, there are a range of paths you can take on this journey. Whether you’re just beginning to explore reproductive health or have been searching for solutions for a while, this guide aims to provide clarity and reassurance as you get closer to your dream of starting a family.
With a better understanding of these uterine issues, you’ll feel more empowered to make informed decisions and seek the proper support from fertility specialists and treatment options that suit your needs. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey—there’s help and hope available every step of the way.
Part 1: Understanding Uterine Abnormalities
Fertility challenges can arise from various factors, with uterine abnormalities being among the most significant. The structure and function of the uterus are vital for conception and maintaining a pregnancy. When the uterus develops abnormally or undergoes changes over time, it can affect your ability to conceive or carry a pregnancy to term. Understanding the different types of abnormalities helps in recognising the potential hurdles and exploring suitable treatments.
1.1 Common Types of Abnormalities
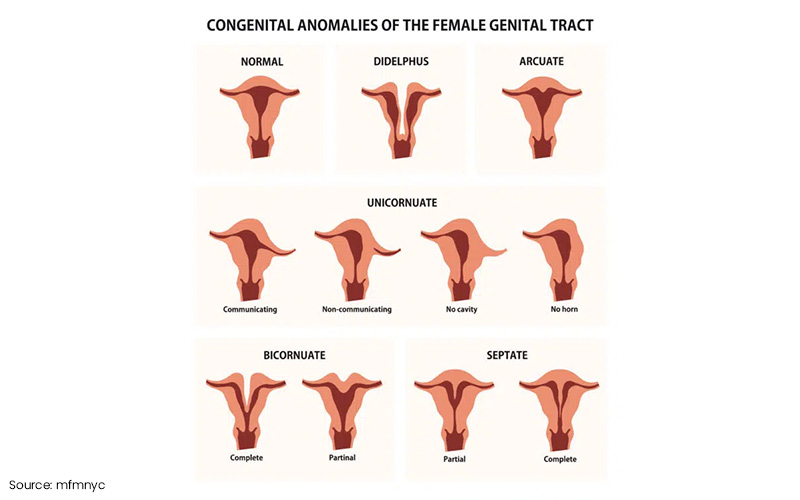
Uterine abnormalities typically fall into three categories: congenital (present from birth), acquired (developing later in life), and endometrial abnormalities, which specifically affect the uterine lining. Here’s a closer look at each type:
- Congenital Abnormalities (Present from Birth)
-
Bicornuate Uterus
A bicornuate uterus is heart-shaped, with two separate cavities instead of the typical single space. This can affect embryo implantation and may increase the risk of preterm labour. While some women with a bicornuate uterus can carry a pregnancy to term, others might face recurrent pregnancy losses due to the irregular shape of their uterus.
-
Septate Uterus
In a septate uterus, a fibrous or muscular wall (known as a septum) divides the uterus into two sections. This can interfere with implantation, leading to recurrent miscarriages, as the embryo may struggle to attach to the uterine wall. Surgical removal of the septum is often recommended to enhance fertility outcomes and improve the chances of a successful pregnancy.
-
Unicornuate Uterus
With a unicornuate uterus, only one side of the uterus develops, significantly limiting the space available for a growing embryo. This condition can often lead to miscarriages or complicated pregnancies. Infertility treatments may be necessary to improve the chances of conception and achieve a healthy pregnancy.
-
Didelphic Uterus
The didelphic uterus is a rare congenital abnormality where the uterus is completely divided into two separate cavities, and it may even feature two cervixes or vaginas. This condition can heighten the risk of miscarriage, preterm birth, and complications during conception and pregnancy maintenance. Women with a didelphic uterus often require more frequent monitoring throughout their pregnancy to manage potential risks effectively.
-
- Acquired Abnormalities (Develop Over Time)
-
Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are benign tumours that form inside or on the surface of the uterus. Depending on their size and location, fibroids may obstruct implantation, distort the shape of the uterine cavity, or block the fallopian tubes, leading to infertility. However, many women with fibroids can successfully conceive after treatments like myomectomy or assisted reproductive techniques (ART).
-
Polyps
Uterine polyps are benign growths that form in the uterine lining. They can interfere with embryo implantation and cause irregular bleeding, both of which can affect fertility. Treatment usually involves removing these polyps, helping to restore a more suitable environment for conception.
-
Adhesions (Asherman’s Syndrome)
Adhesions, or scar tissue within the uterus, can develop after surgery or infection, such as following a dilation and curettage (D&C) procedure. These adhesions may block the uterine cavity, resulting in fertility issues. Removing scar tissue through hysteroscopic surgery can significantly improve the chances of successful conception.
-
Hydrosalpinx
This condition occurs when the fallopian tubes are blocked and filled with fluid, often due to infection or prior surgery. The fluid can leak into the uterus, preventing implantation or leading to miscarriage. Treatment for hydrosalpinx typically involves surgical intervention, such as removing the affected tubes, followed by ART treatments.
-
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis happens when the endometrial tissue, which usually lines the uterus, grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. This can cause the uterus to enlarge, leading to symptoms like heavy bleeding and pain. Adenomyosis can interfere with implantation or embryo development, impacting fertility. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of symptoms and may include medication or surgery to improve reproductive outcomes.
-
- Endometrial Abnormalities
-
Thin Endometrial Lining
The endometrial lining is crucial for embryo implantation. If it is too thin, it may not provide the necessary support for a fertilised embryo, making it difficult to achieve or maintain a pregnancy. Hormonal treatments or specialised fertility techniques, such as egg freezing in Singapore, may be recommended to enhance the chances of a healthy pregnancy.
-
Endometrial Scarring
Scar tissue within the endometrium, often caused by surgery or infection, can interfere with implantation. Similar to Asherman’s syndrome, this condition usually requires surgical intervention to remove the scar tissue, restoring a more supportive uterine environment for conception. Following this, fertility treatments can help in achieving pregnancy.
-

1.2 How Uterine Abnormalities Impact Fertility
Uterine abnormalities can affect fertility in various ways, often making it challenging to conceive or maintain a healthy pregnancy. While some women might not notice symptoms until they encounter difficulties with pregnancy, understanding how these conditions affect conception is essential for finding effective treatments. Below, we discuss the primary ways the abnormalities impact fertility.
-
Interruption of Embryo Implantation
One of the most immediate ways uterine abnormalities affect fertility is by disrupting embryo implantation. For conception to occur, a fertilised embryo must attach itself to the uterine lining and begin to grow. Structural issues like fibroids, a septate uterus, or polyps can prevent this crucial process from happening.
Fibroids, for example, can create physical barriers within the uterus, preventing the embryo from reaching the endometrial lining or distorting the shape of the uterine cavity, making implantation more challenging.
With a septate uterus, the wall of tissue dividing the uterine cavity may result in repeated implantation failures or recurrent miscarriages. Fortunately, surgical removal of the septum can significantly improve fertility outcomes.
Polyps can also interfere with implantation by altering the endometrial surface, disrupting the nurturing environment needed for the embryo to attach and grow.
-
Effects on the Uterine Environment
The shape and structure of the uterus play a vital role in the success of a pregnancy. Abnormalities can create less-than-ideal conditions for embryo development and overall pregnancy success.
Take, for instance, a bicornuate uterus, which divides the uterine cavity into two horns. This heart-shaped uterus reduces the available space for the embryo to grow, potentially leading to complications like miscarriage or preterm birth.
In conditions such as adenomyosis, where the endometrial tissue grows into the muscular wall of the uterus, the organ can become enlarged and inflamed. This can result in painful symptoms and hinder the uterus’s ability to nurture an embryo, making conception more difficult.
These structural abnormalities, whether congenital or acquired, can create an environment that is less hospitable for a fertilised egg. Even if implantation occurs, the altered conditions can increase the risk of complications, such as miscarriage or poor foetal development.
-
Impact on Pregnancy Maintenance
Uterine abnormalities not only affect the early stages of conception; they can also present significant challenges in maintaining a pregnancy. Once an embryo implants, the uterus needs to provide a stable and supportive environment for the developing foetus. However, certain abnormalities can disrupt this process, leading to miscarriages or preterm deliveries.
Fibroids can complicate pregnancy, especially if they grow larger or are located in areas that impede the foetus’ growth. Their presence can increase the likelihood of miscarriage or lead to issues like abnormal positioning of the baby, which may require interventions such as a C-section.
Adhesions, or scar tissue, can restrict the uterine cavity, limiting the space available for the growing foetus and making it harder for the uterus to expand as needed. This can result in complications such as preterm birth or difficulties in carrying the pregnancy to term.
For women facing these challenges, maintaining a healthy pregnancy often involves close monitoring and, in some cases, medical intervention. ART treatments such as IUI or IVF may be recommended to enhance the chances of conception and reduce the risks associated with these abnormalities.
1.3 Diagnostic Techniques
Early diagnosis of the abnormalities is crucial for managing fertility issues and determining the most effective treatment options. Thanks to reproductive health, specialists have a range of diagnostic techniques at their disposal, allowing them to identify these abnormalities and provide tailored solutions accurately. Here’s an overview of the most common diagnostic approaches used to detect these conditions.
-
Ultrasound Scans and Hysterosonography
One of the first tools used to diagnose uterine abnormalities is the pelvic ultrasound. This non-invasive imaging technique allows specialists to examine the uterus, ovaries, and other pelvic organs. Using high-frequency sound waves, a pelvic ultrasound produces images that can reveal issues like fibroids, polyps, and other structural abnormalities. The procedure is quick, painless, and provides immediate insights into the condition of your uterus.
For a more detailed view, doctors may recommend hysterosonography. In this procedure, saline is injected into the uterus during an ultrasound to expand the uterine cavity. This added fluid improves the clarity of the images, enabling specialists to identify abnormalities, such as endometrial polyps or adhesions, that might not be visible during a standard ultrasound.
-
Hysteroscopy and Laparoscopy
When a more thorough examination is required, procedures like hysteroscopy and laparoscopy can be performed to visually inspect the inside and outside of the uterus.
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a thin, lighted tube called a hysteroscope to look inside the uterine cavity. This allows specialists to detect abnormalities like polyps, adhesions, or a septate uterus. In some instances, minor issues can even be addressed during the procedure, such as removing polyps or breaking up adhesions, which can provide immediate relief and help with diagnosis.
Laparoscopy, in contrast, involves making small incisions in the abdomen and inserting a camera to examine the outside of the uterus and surrounding organs, including the ovaries and fallopian tubes. This procedure is particularly effective for diagnosing conditions like fibroids, endometriosis, or congenital abnormalities, such as a bicornuate or unicornuate uterus. While laparoscopy is more invasive than hysteroscopy, it offers a comprehensive view of the reproductive organs and can help identify complex or less obvious conditions affecting fertility.
-
MRI and Advanced Imaging Techniques
For more detailed imaging, particularly when diagnosing complex abnormalities, specialists may recommend Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Unlike ultrasounds, MRIs use magnetic fields and radio waves to produce highly detailed images of the uterus and surrounding tissues. This technique is especially useful for identifying conditions like adenomyosis or congenital defects that may not be as visible through other imaging methods. MRI provides a deeper look at the structural aspects of the uterus, aiding specialists in planning appropriate treatment.
Another imaging tool that might be used is the 3D ultrasound, which offers a more thorough view of the uterine structure compared to standard 2D ultrasounds. This technique is particularly effective in diagnosing abnormalities related to uterine shape, such as a bicornuate or septate uterus. With 3D imaging, specialists can better assess the severity of the abnormality and plan more precise interventions.
-
When to Consult a Specialist
If you are experiencing difficulties in conceiving or have experienced recurrent miscarriages, it might be time to consult a specialist at a fertility clinic. These experts are equipped to investigate and diagnose uterine abnormalities that could be affecting your fertility. Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention, which can increase your chances of conceiving.
Other signs that may suggest a uterine abnormality include abnormal bleeding, severe menstrual pain, and irregular periods. If you experience any of these symptoms, seeking professional advice is essential, as they could indicate an underlying condition affecting your reproductive system.
Timely consultation and diagnosis can provide clarity, guide treatment options, and offer reassurance as you navigate the path toward parenthood. Whether you’re considering options like IUI or IVF, understanding the health of your uterus is a vital part of optimising your chances for a successful pregnancy.

Part 2: Treatment Options for Uterine Abnormalities and Infertility
When the abnormalities affect fertility, it can feel overwhelming. Thankfully, effective treatments are available to help individuals and couples pursue their dream of parenthood. Depending on the type and severity of the abnormality, surgical interventions may be necessary to address structural issues that hinder conception or the maintenance of pregnancy. Here, we’ll explore some common surgical treatments that can correct these issues and improve fertility outcomes.
2.1 Surgical Interventions
Surgical procedures can effectively address various uterine abnormalities, from fibroids and polyps to congenital issues like a bicornuate or septate uterus. Each surgery comes with its own methods, recovery processes, and potential success rates, all tailored to the specific issue being addressed.
-
Hysteroscopic Surgery for Fibroids and Polyps
Hysteroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive technique designed to remove fibroids and polyps from the uterine cavity. During this procedure, a hysteroscope is gently inserted through the vagina into the uterus, allowing the surgeon to see and remove the growths without making any external incisions. This precise approach targets only the abnormal tissue, minimising trauma to surrounding areas.
Fibroids and polyps can block the uterine cavity and interfere with embryo implantation, creating an unfavourable environment for conception. Removing these growths helps create a more supportive environment for pregnancy, potentially increasing the chances of success. Most patients find that recovery from hysteroscopic surgery is quick, often returning to their normal activities within a few days. While mild discomfort, cramping, or spotting may occur after the procedure, these symptoms typically fade within a week. For many, the removal of fibroids or polyps can significantly enhance fertility, particularly when these growths were the main barriers to conception. However, individual factors such as age, the size and location of the growths, and overall uterine health will influence the extent of improvement.
-
Laparoscopic Surgery for Congenital Abnormalities
Laparoscopic surgery is another minimally invasive technique used to correct congenital abnormalities such as a bicornuate or septate uterus. During the procedure, the surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen and inserts a laparoscope—a thin tube equipped with a camera. This allows for a clear view of the reproductive organs, enabling the surgeon to perform necessary repairs, like reshaping or dividing the uterine cavity.
Congenital abnormalities can create structural challenges within the uterus, making it difficult for some individuals to carry a pregnancy to term. Laparoscopic surgery aims to address these issues, enhancing the uterine environment for embryo implantation and supporting pregnancy maintenance. Recovery times can vary based on the complexity of the surgery, but most patients are able to return to their regular activities within a few weeks. While some may experience mild pain or discomfort at the incision sites, these symptoms are generally manageable. This type of surgery has the potential to significantly improve fertility, particularly for those facing congenital challenges, increasing the chances of both conception and carrying a pregnancy to full term. Nevertheless, success rates may vary depending on the specific abnormality and the individual’s overall gynaecological health.
-
Surgical Correction of Adhesions and Scarring
For patients dealing with adhesions or scar tissue—often associated with Asherman’s syndrome—surgery can offer a path to restore normal uterine function. This procedure may involve hysteroscopy or laparoscopy, depending on where the adhesions are located and how severe they are. By carefully removing the scar tissue, the surgeon aims to clear any blockages in the uterine cavity that could hinder embryo implantation, ultimately helping to restore the uterus to its natural shape and function.
Recovery from adhesion surgery is generally quick, with many patients able to return to their regular activities within a week or two. While some may experience mild discomfort, cramping, or spotting, these symptoms typically resolve swiftly. For many individuals, removing adhesions can lead to a significant improvement in fertility, as it eliminates physical barriers that prevent pregnancy. The extent of this improvement can vary, depending on the severity of the scarring and the overall health of the reproductive system.
-
Success Rates and Potential Risks of Surgery
Success rates for surgical interventions can vary significantly based on the type of uterine abnormality, the specific procedure performed, and individual factors such as age and overall gynaecological health. For many patients, surgery can lead to a substantial improvement in fertility and enhance the chances of a successful pregnancy.
However, like any surgical procedure, these interventions carry potential risks, including infection, bleeding, and anaesthesia-related complications. There’s also a chance that new scar tissue might develop post-surgery, which could impact future fertility. It is crucial to have an open and honest discussion with your OBGYN specialist about the risks and benefits of surgery. This conversation can help you determine if surgery is appropriate for your unique situation, ensuring you feel informed and supported throughout the process.
2.2 Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ART)
ART treatments provide various solutions for individuals and couples navigating fertility challenges. For those with uterine abnormalities, combining ART options such as IUI and IVF with surgical interventions can significantly improve the chances of conception. In Singapore, ART services are readily accessible, with the necessary technology and high standards of care to support fertility treatments.
-
Overview of IUI and Success Rates
IUI fertility treatment is a less invasive option designed to help individuals and couples struggling with infertility. During this procedure, sperm is collected, processed, and then placed directly into the uterus around the time of ovulation. This targeted approach increases the number of healthy sperm reaching the egg, enhancing the chances of fertilisation. IUI is often recommended for those with unexplained infertility or mild male-factor infertility, where sperm motility or count may be lower than average.
While the success of IUI varies, several factors influence the outcome. Age plays a significant role, with individuals under 35 typically experiencing higher success rates compared to those over 40. Other factors, such as the underlying cause of infertility and sperm quality, also contribute. On average, IUI success rates range from 10% to 20% per cycle. Although this method has lower success rates compared to advanced ART options like IVF, IUI is often a sensible first step for less complex cases. It offers a more affordable and less invasive approach, requiring fewer medications and less monitoring than IVF, making it a more accessible option for those embarking on their fertility journey.
-
Explanation of IVF
IVF treatment in Singapore is a more intricate approach to fertility, designed for individuals facing complex challenges or those who haven’t found success with other methods. The process begins with stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, which are then surgically retrieved and fertilised with sperm in a laboratory. Once fertilisation occurs, embryos develop and are monitored for a few days before the healthiest ones are selected for transfer back into the uterus, aiming for successful implantation.
One prominent feature of IVF is that it has generally higher success rates compared to IUI, especially for those dealing with significant issues like blocked fallopian tubes, severe male-factor infertility, or advanced maternal age. Factors such as age, egg and sperm quality, and specific fertility challenges can influence these rates.
For younger patients, IVF success rates can be as high as 40% to 50% per cycle, though they may decrease with age or other complications. Additionally, IVF offers essential benefits, including the option for preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) to identify any chromosomal abnormalities in embryos before transfer. It also allows the use of donor eggs or sperm and provides the option to freeze embryos for future use. Overall, IVF presents a comprehensive solution for a wide array of infertility issues, including those related to previously corrected uterine abnormalities.
-
Combining ART with Surgery for Uterine Abnormalities
Combining surgical intervention with ART techniques such as IUI or IVF can provide a tailored solution for individuals facing uterine abnormalities. Surgery addresses structural issues that may be hindering fertility, such as fibroids, polyps, or adhesions. Once the abnormalities are addressed, ART can be used to facilitate conception, as the improved uterine environment may now be more conducive to successful implantation.
This dual approach often enhances the chances of success for many patients. Surgery tackles the root cause of the problem, while ART maximises the potential for conception afterwards. For instance, correcting a septate uterus can significantly reduce the risk of miscarriage, and IVF can ensure that healthy embryos are placed in a now-optimised uterine cavity. A coordinated treatment plan like this is particularly beneficial for individuals who have experienced recurrent pregnancy loss or who have structural issues contributing to their infertility.
Before recommending a specific ART method, a fertility specialist will carefully evaluate the patient’s medical history, surgical needs, and fertility goals. Personalising the approach ensures that the treatment plan effectively addresses both anatomical and reproductive challenges, increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy.
-
The Role of Fertility Preservation, Including Egg Freezing
Fertility preservation has gained significant importance in recent years, especially for individuals who want to delay pregnancy or face medical treatments that could affect their fertility, such as chemotherapy for cancer. One of the most popular options is egg freezing or cryopreservation. This technique involves stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, retrieving them, and then freezing them for future use. By preserving their eggs during their most fertile years, individuals can keep their options open and choose to pursue pregnancy later in life.
The egg freezing process is similar to IVF. After stimulating the ovaries and retrieving the eggs, advanced cryopreservation techniques are used to freeze them. When individuals are ready to try for a baby, these frozen eggs can be thawed, fertilised, and implanted through IVF. This method is particularly beneficial for those dealing with medical conditions like endometriosis or autoimmune disorders that might impact their future fertility. For many, the ability to preserve fertility offers peace of mind and the flexibility to plan for pregnancy based on personal or medical circumstances. In Singapore, comprehensive fertility preservation services are available, and discussing the best timing for egg freezing with a specialist can help maximise success rates in the future.

2.3 Holistic Care and Management
Infertility treatments go beyond the medical aspects; they involve emotional, mental, and lifestyle changes that are crucial for maximising the chances of success. Adopting a holistic approach that combines psychological support, healthy lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring can greatly improve both the treatment experience and its outcomes. Recognising the emotional toll this journey can take is essential, and having a supportive network can make a world of difference in navigating the ups and downs along the way.
-
The Need for Psychological Support in Fertility Treatment
The emotional impact of fertility treatments can be incredibly overwhelming. The anticipation, uncertainty, and potential setbacks often lead to stress, anxiety, and mood swings, which can take a significant toll on mental health. This emotional strain doesn’t just affect the person undergoing treatment; it also extends to their partner and family. The rollercoaster of feelings that accompanies fertility cycles—whether through IUI, IVF, or surgical interventions—can leave individuals feeling isolated and helpless, grappling with a range of emotions that can be hard to navigate.
This is where professional psychological support becomes crucial. Counsellors or therapists who specialise in fertility issues provide a safe space for individuals and couples to express their feelings and develop effective coping strategies. Joining support groups can also be incredibly beneficial, offering a sense of community and understanding from others who are facing similar challenges. These resources are essential for helping individuals manage the ups and downs of treatment, easing anxiety, and building resilience throughout their fertility journey.
-
Lifestyle Modifications and Their Role in Fertility Improvement
Embracing a healthy lifestyle can have a significant positive impact on fertility. A well-balanced diet filled with essential nutrients supports hormonal balance and overall reproductive health. Foods rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and vitamins such as folic acid, zinc, and omega-3s can help boost fertility. Regular exercise also plays a vital role, as it helps regulate hormones and improves circulation—both key factors for gynaecological health. However, finding the right balance is crucial; excessive exercise can sometimes have the opposite effect on fertility, so moderation is essential.
Reducing or eliminating harmful substances like alcohol, tobacco, and recreational drugs can greatly enhance fertility outcomes. Smoking and heavy drinking have been linked to lower sperm quality, reduced ovarian function, and a higher risk of miscarriage. Making conscious lifestyle adjustments, such as cutting back on these substances, can significantly improve the effectiveness of the treatments and enhance their overall health.
Additionally, managing stress is equally important, as it can disrupt hormone levels and interfere with ovulation or sperm production. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing into daily routines can foster a more balanced state, promoting better fertility. Engaging in enjoyable activities and maintaining social connections also play a crucial role in reducing stress during this challenging journey.
-
Regular Monitoring and Consultations with a Specialist
Routine Check-ups:
Regular monitoring is critical in managing infertility. Scheduled check-ups with a specialist help track progress and identify any potential issues early on. These consultations allow continuous adjustments to treatment plans, ensuring they remain optimised for the individual’s evolving health and circumstances. Monitoring hormone levels, follicle development, and the uterine lining can help determine whether the treatment is progressing as hoped.
Fertility is a deeply personal journey, and ongoing consultations with a fertility specialist allow for a truly tailored approach to care. This personalised strategy means that treatments can be adjusted to meet each patient’s specific needs. Whether it’s fine-tuning medication dosages, scheduling additional tests, or modifying the timing of procedures, having a close partnership with a fertility doctor dramatically increases the chances of successful outcomes. This collaborative approach ensures that any changes in the patient’s condition are addressed promptly, allowing the care plan to remain relevant and effective throughout the treatment journey.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. What are the most common uterine abnormalities that affect fertility?
Some common abnormalities that can impact fertility include fibroids, which are non-cancerous growths in the uterus, and polyps, which are small growths on the uterine lining. Conditions like a septate uterus, where the uterus is divided by a wall, or a bicornuate uterus, which has a heart-shaped appearance, can also make it harder for an embryo to implant properly. Each of these conditions affects the uterus in different ways, and their impact on fertility can vary.
2. Can I still get pregnant with a uterine abnormality?
Yes, you can still get pregnant with a uterine abnormality. Many women with these conditions go on to have successful pregnancies. Treatments like surgery to correct the abnormality or assisted reproductive techniques, such as IVF, can improve your chances of conception. It’s essential to work closely with a fertility specialist who can guide you through the appropriate options for your specific situation.
3. What are the risks associated with infertility treatments for women with uterine abnormalities?
Infertility treatments for women with uterine abnormalities can involve some risks, like a higher chance of multiple pregnancies or complications during pregnancy. However, these risks are often manageable with careful monitoring and personalised care from your healthcare team. Discussing your concerns with a specialist can help you understand and mitigate these risks, giving you a clearer picture of what to expect.
4. When should I consider egg freezing?
Egg freezing might be an option if you’re facing treatments or conditions that could impact your future fertility or if you’re not ready to start a family at the moment but want to keep your options open. It’s also a thoughtful choice if you’re planning for the future and want to preserve your fertility while you’re still young and healthy. Consulting with a fertility specialist in Singapore can help you decide if this is the right step based on your circumstances.

While uterine abnormalities can present challenges on the path to pregnancy, understanding your condition and exploring available treatments can significantly improve your chances of achieving a positive outcome. Knowledge is power, and being informed about your options enables you to make confident decisions regarding your reproductive health.
With a range of conception support, including surgical interventions, assisted reproductive techniques, and holistic care, you can find a path that suits your individual needs and maximises your chances of realising your dream of parenthood. Each approach has unique benefits tailored to help you start or expand your family.
If you have concerns about uterine abnormalities or need guidance on the optimal approach for your situation, our dedicated team at The O&G Specialist Clinic is here to support you. We understand the emotional and physical toll that fertility challenges can take, which is why we prioritise compassionate care and personalised advice. Contact us today to schedule a consultation; we’re here to help you every step of the way.